Migrate to Kubernetes
1. Copy docker-compose services data to local storage
Stop Hyperscale services so that all of the product's state is flushed to persistent storage. You must run the below command from the same directory where the docker-compose.yaml file exists.
docker-compose stopCreate folders for data backup of all services.
mkdir container_data
cd container_data/
mkdir controller
mkdir unload
mkdir masking
mkdir load
mkdir proxy
cd ../Copy the SQLite database file and encryption key Docker volume folder data on a local machine in the created folder.
docker ps -a // list out the name of containers
docker cp <controller-service-container-name>:/data ./container_data/controller/
docker cp <unload-service-container-name>:/data ./container_data/unload/
docker cp <load-service-container-name>:/data ./container_data/load/
docker cp <masking-service-container-name>:/data ./container_data/masking/
eg: docker cp hyperscale-masking_controller-service_1:/data ./container_data/controller/Copy the SSL certificates Docker volume folder data on a local machine in the created folder (This step is only required if custom certificates are used).
docker cp <proxy-container-name>:/etc/config/nginx/ssl ./container_data/proxyAll the container_data files should be as below.
├── controller
│ └── data
│ └── db.sqlite
├── load
│ └── data
│ ├── db.sqlite
│ └── encryption.key
├── masking
│ └── data
│ ├── db.sqlite
│ └── encryption.key
├── proxy
│ └── ssl
│ ├── dhparam.pem
│ ├── nginx.crt
│ ├── nginx.key
│ └── ssl.conf
└── unload
└── data
├── db.sqlite
└── encryption.keyGrant permission 770 to all files.
chmod 770 -R .Please note that docker-compose log files will not be migrated so keep the backup, of log files before starting the migration process.
2. Restore docker-compose services data to Hyperscale deployed on the Kubernetes setup (in Persistent Volume)
Install the required version of the Hyperscale Compliance Engine using Kubernetes. For more information about the installation steps, refer to the Installation and Setup section.
List the pods name for further reference:
kubectl get pods -n hyperscale-servicesRestore Hyperscale docker-compose version volume data with Hyperscale deployed on the Kubernetes setup (in Persistent Volume).
Execute the below process for all the pods names except the proxy pod to copy each service data.
cd container_data/<service- folder-name>
kubectl cp data hyperscale-services/<service-pod-name>:/
eg:
cd container_data/masking
kubectl cp data hyperscale-services/masking-service-7788ccbbbb-lnzhv:/3. List out deployment names and restart all the services using kubectl rollout.
kubectl get deployments -n hyperscale-services
kubectl rollout restart deployment <controller-service-deployment-name> -n hyperscale-services
eg: kubectl rollout restart deployment controller-service -n hyperscale-services4. Update the SSL certificates (This step is only required if custom certificates are used).
Go to container_data/proxy/ssl folder and get the base64 value of nginx.crt, nginx.key, and dhparam.pem. For example:
cat nginx.crt | base64 | awk '{print}' ORS='' | awk '{print}'Now update the base64 value of each in k8 values.yaml file.
5. Update the other user-configurable properties from docker-compose .env file to values.yaml accordingly
All the available configurations can be found at Configuration settings. The configuration migration is divided into two steps:
Modify existing configuration for any service:
Go to the hyperscale-helm chart directory. Under the templates folder, locate the corresponding <service-name>-deployment.yaml file. For more details, refer to the below screenshot.
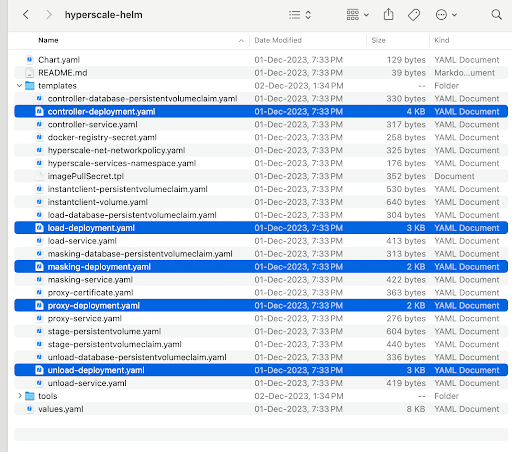
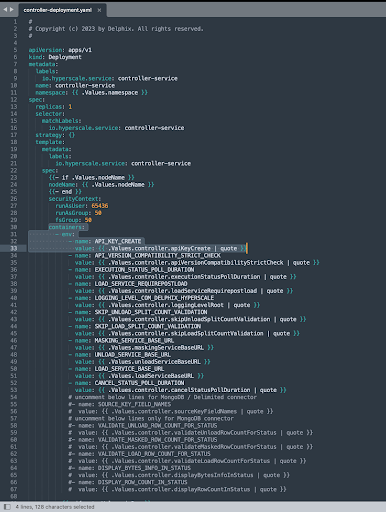
Open the corresponding <service-name>-deployment.yaml file for which you want to modify the new configuration.
Example: Let’s suppose you want to change the config value for API_KEY_CREATE in controller-deployment.yaml file. As you can see that API_KEY_CREATE config value is mapped with Values.controller.apiKeyCreate.
Now under the hyperscale-helm chart directory, open the values.yaml file and search for apiKeyCreate property of controller attribute and change the corresponding value.
Add a new configuration for any service
In case the configuration name doesn’t exist in <service-name>-deployment.yaml file, add your configuration as part of env in <service-name>-deployment.yaml file and also define config with the same name in values.yaml corresponding to the service environment as explained above, to get the values from values.yaml file.
Apply helm upgrade to reflect the new values.yaml file changes.
helm upgrade hyperscale-helm -f hyperscale-helm/values.yaml hyperscale-helmYour docker-compose Hyperscale VM is now fully migrated to Kubernetes Hyperscale VM. Check the k8 running pods, like below:
delphix@hyperscale-k8s:~/_database$ kubectl get pods -n hyperscale-services
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
masking-service-7788ccbbbb-lnzhv 1/1 Running 0 4h28m
unload-service-5f9946556f-4qg7l 1/1 Running 0 4h28m
proxy-767d6ccbdd-2vdhv 1/1 Running 0 4h28m
load-service-5bb994dbbf-c85mz 1/1 Running 0 3h43m
controller-service-6c6df56bbd-blng6 1/1 Running 0 62mIf apiKeyCreate property is defined as true in values.yaml, then you can get the API-Key as below to access the API. In case, apiKeyCreate property is defined as false then you can use your existing API-Key.
kubectl logs <controller-pod-name> -n hyperscale-services | grep 'NEWLY GENERATED API KEY' | sed 's/^.*: //'