Hyperscale Compliance architecture
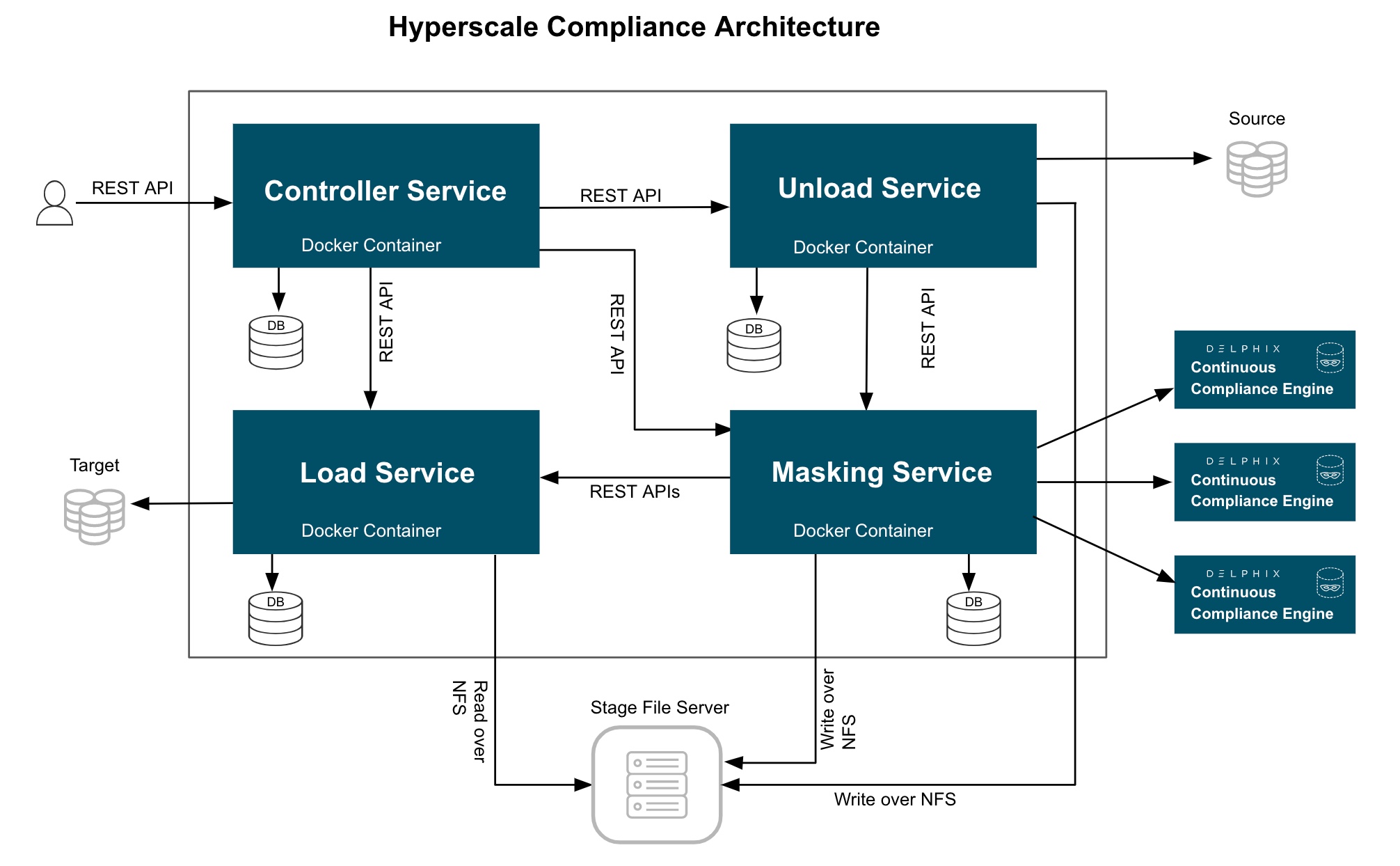
The Hyperscale Compliance architecture comprises four components mainly; Controller Service, Unload Service, Masking Service, and Load Service.
Controller service
The following are the main functions of a controller service:
Exposes user-accessible API.
Once the controller service receives user requests (for example, register engine, create a dataset, create a connector, create Job, etc.), it will split the request and sends a request for further processing to downstream services (Unload, Masking, Load) and once response is received from downstream service, the same will be processed by controller service and returned to the user.
The controller service accepts request job execution from the user and invokes the job execution process by invoking unload service asynchronously.
The controller service will keep polling data job execution data from the downstream service until execution completes.
The controller service will also determine the status of job execution and store execution data in the database.
Controller service allows you to restart a failed (Failed during File Loader, Post Load) execution
Unload service
The following are the main functions of a unload service:
Exposes APIs that are accessible to internal services only.
Unload service exposes required APIs that help the caller (controller service) to create required inputs (source info, dataset, etc.) for job execution.
Unload service exposes an API to trigger unload from the source data source. As part of the unload process, it performs the following operations:
Reads metadata of source data source (e.g. number of rows in a source file/table) and stores that in the unload service database.
Reads data from source data source parallelly (by starting multiple parallel processes for each source entity like tables in case of a relational database ) and stores this data in
.csvfiles.Once data is loaded into one
.csvfile, unload service triggers the masking service to start the masking process for that*.csvfile.
For running execution, Unload service maintains metadata data (number of rows processed, table/file names processed, etc.) in its database. This data can be retrieved by calling an API.
Once execution completes execution data in the database and file system gets cleaned by invoking the corresponding API.
Masking service
The following are the main functions of a masking service:
Exposes APIs that are accessible to internal services only.
Masking services expose required APIs that help the caller (controller service) to create required inputs (Continuous Compliance engine info, dataset, job, etc.) for job execution.
Masking service exposes an API to trigger the masking process. As part of the masking process, it performs the following operations after receiving a masking request from unload service for a CSV file:
Based on Intelligent load balancing, create and start jobs for unloaded files on Continuous Compliance Engines (based on the capacity of Continuous Compliance Engines associated with the hyperscale job).
Monitor Continuous Compliance Engine jobs triggered in the previous step.
Once monitoring determines that a Continuous Compliance Engine has successfully masked the file, send an async request to the load service (to load data into the target data source) for that masked file.
For running execution, the Masking service maintains metadata data (number of rows processed, table/file names processed, etc.) in its database. This data can be retrieved by calling an API.
Once execution completes execution data in the database and file system gets cleaned by invoking the corresponding API.
Load service
The following are the main functions of a Load service:
Exposes APIs that are accessible to internal services only.
Load service exposes required APIs that help the caller to create required inputs (target data source info, dataset, job, etc.) for job execution.
Load service exposes an API to trigger the Load process. As part of the Load process, it performs the following operations after receiving a load request from the masking service for a masked CSV file:
Perform preload step (for example, cleaning up the target directory or disabling constraints/triggers/indexes). These may be performed once for an execution process (not for each request from the masking service).
Load masked files into the target data source.
Once Loading for a masked is completed, the metadata for this “file load“ will be stored in the load service database.
For running execution, the Load service maintains metadata data (number of rows processed, table/file names processed, etc.) in its database. This data can be retrieved by calling an API.
Once execution completes execution data in the database and file system gets cleaned by invoking the corresponding API.
If the Load service is for a data source that requires post-load steps (e.g. Oracle, MS SQL), then it will include post-load steps which will be triggered by the controller service once all files are successfully loaded into the target data source.
Load service also allows restarting for the post-load step, if post-load fails for an execution.
